Ecosystem
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment; a complex network or interconnected system.
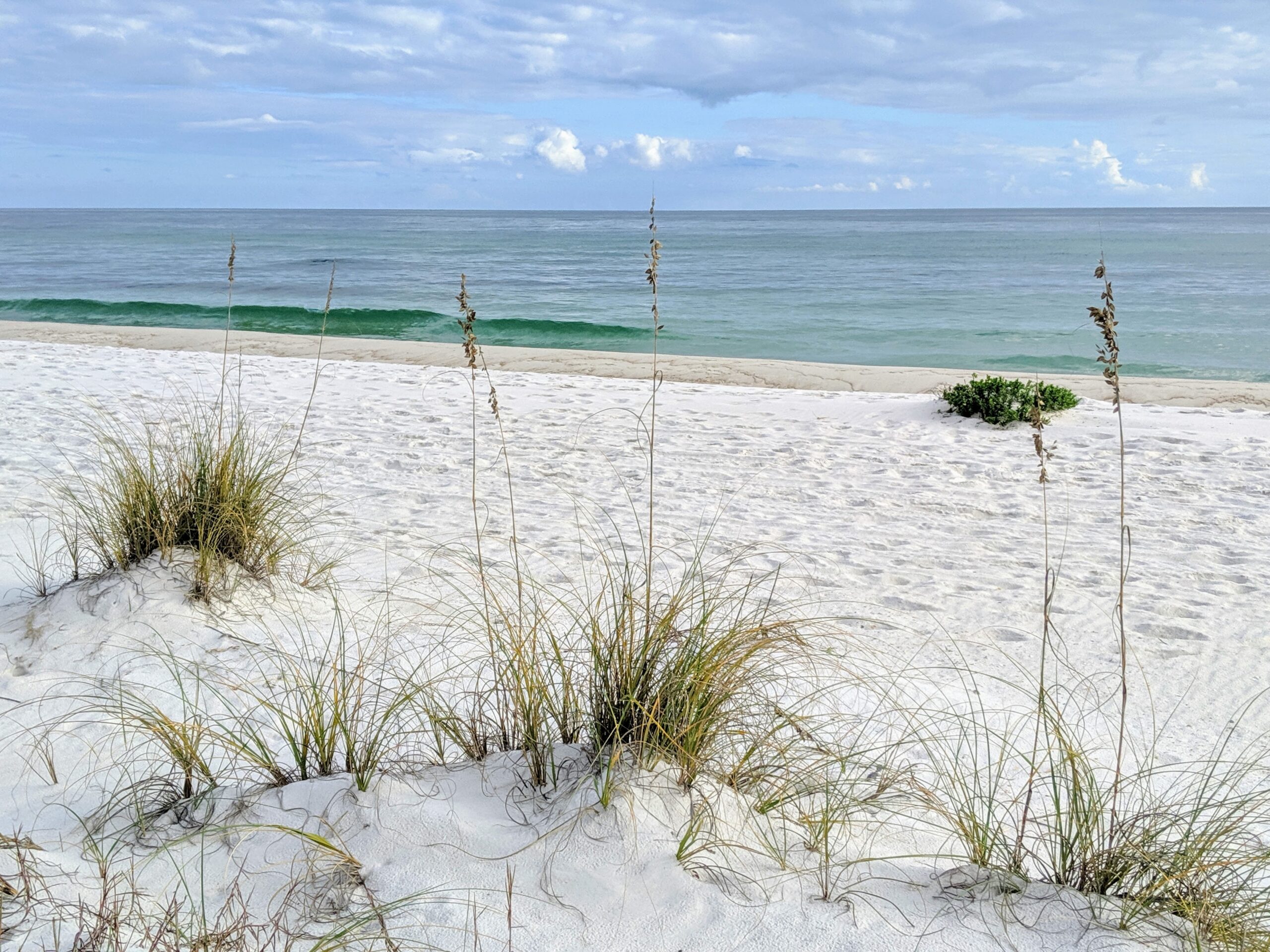
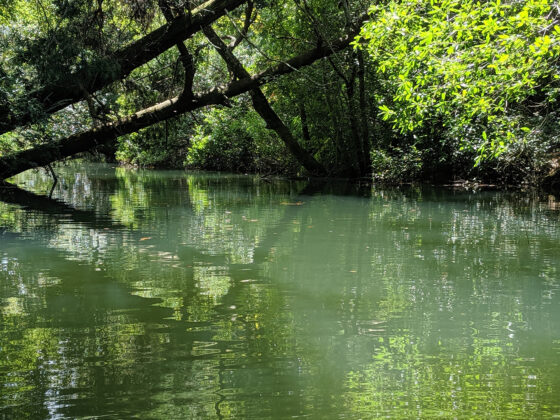
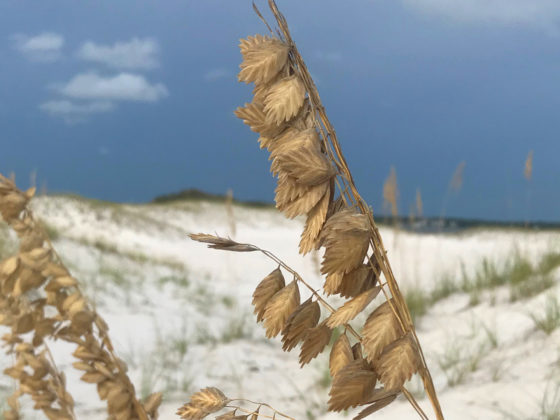
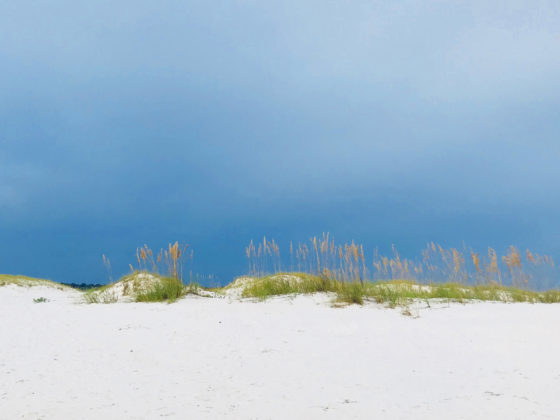
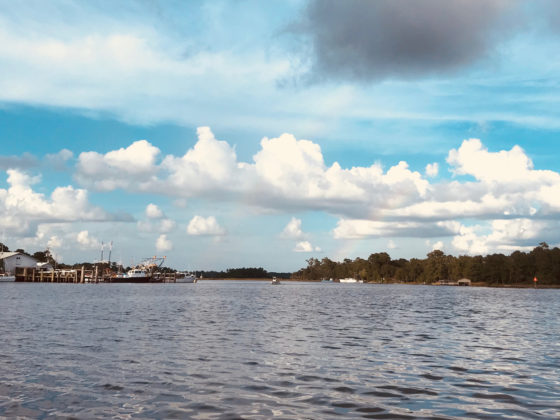
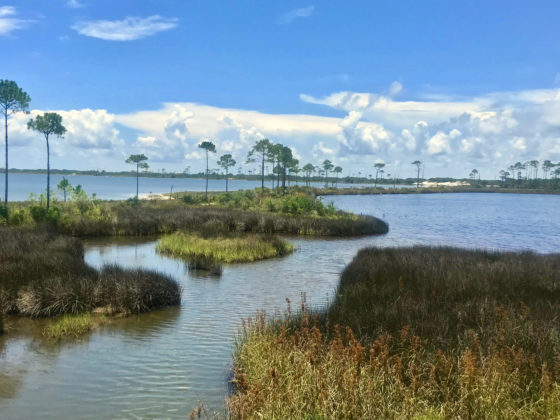
Famous for its beautiful, sugar-white sand beaches, the Gulf of Mexico is a perfect place for groups to retreat to nature and learn while they explore. Deemed “The Amazon of North America,” and the most diverse state east of the Mississippi, the unique ecosystems along the Gulf Coast create living classrooms, ideal for hands-on, experiential learning. Much of the species richness is driven by the thousands of miles of freshwater streams running through this rain-soaked state. As a result, there is an unusually high number of freshwater fish, snails, crayfish, mussels, turtles, and amphibians. Alabama also boasts a variety of geological substrates, which support different ecosystems in sand dunes, bogs, tallgrass prairies, and glades where the bedrock is exposed.
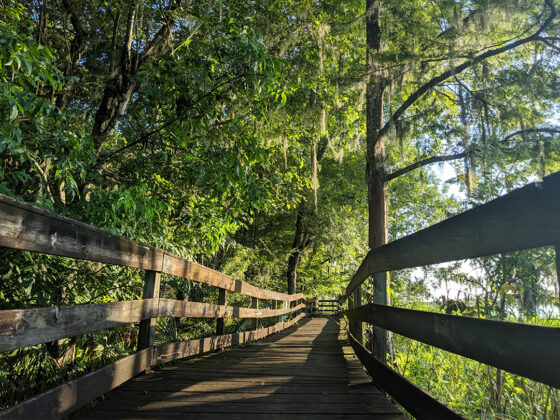
Whether in the forest, on the water, or at the beach, students observe first-hand how each ecosystem they visit, while unique in many ways, functions according to similar ecological principles.